Dive deep into how to make use of your SRS account
Dive deep into how to make use of your SRS account
Let’s talk about SRS, srs-ly!
You may have extra cash idling in the bank account. How about putting them to good use to receive tax relief? If you are worried about low returns, you can even choose to invest those monies and start growing your pool of assets meaningfully. This article will share how you can tap on the Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS) account to kickstart your retirement plan.
So, what is SRS?
The Supplementary Retirement Scheme (SRS) is a voluntary scheme to help individuals prepare for retirement beyond just saving through the regular Central Provident Fund (CPF).
That said, the SRS is not part of your CPF. While CPF requires a compulsory monthly contribution, topping up your SRS account is voluntary and flexible. You may top up your SRS account at any time and as often as you wish, with an annual cap of S$15,300 for Singaporeans/PRs, and S$35,700 for foreigners. Upon hitting the retirement age, an SRS member can enjoy tax-free withdrawals of up to S$40,000 per year over a maximum of 10 years, assuming that the person has no other taxable income.
How does the tax relief work?
You can reduce your taxable income by the same amount that you contributed to your SRS account. In other words, this means that for every S$1 that you put into your SRS account, it will give you S$1 equivalent of tax relief.
Let us put this into an example….
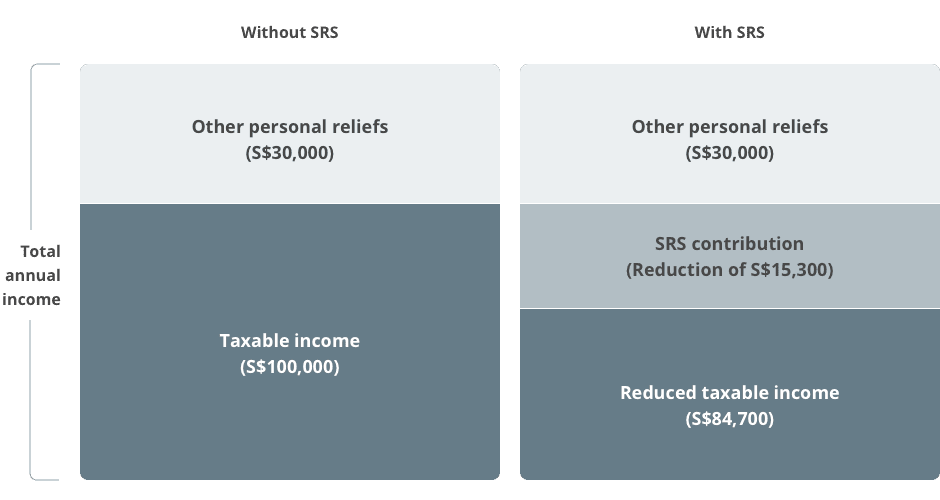
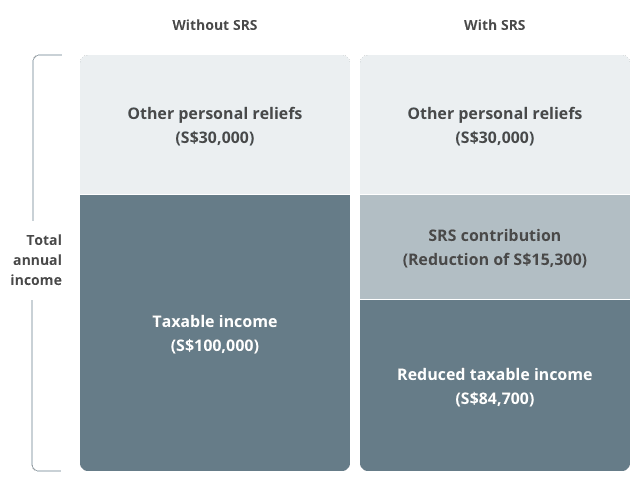
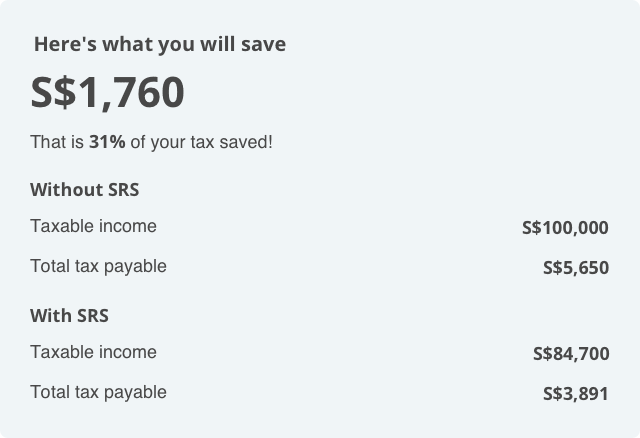
Assuming Kelvin earns an annual income of S$130,000 and has a personal relief of S$30,000. If Kelvin does not contribute to SRS, his taxable income for that particular year would be S$100,000 (S$130,000 − S$30,000).
However, if Kelvin had made an SRS contribution of S$15,300, his taxable income would then be reduced to S$84,700 (S$130,000 − S$30,000 − S$15,300).
How SRS helps you save on tax
The following illustration is based on an annual income of S$130,000 and a personal relief of S$30,000.

Source: OCBC
Based on his income tax bracket, Kelvin could have potentially saved S$1,760 should he contribute S$15,300 to the SRS account in that particular year. That’s some good savings there! Curious to find out how much tax you can potentially save? Try out our SRS savings calculator!
But wait, what’s the catch?
The potential tax savings do sound attractive, but there are 3 things that one should still consider before contributing money into the SRS account.
- There is a maximum annual contribution of S$15,300 for Singaporeans and PRs. Meanwhile, foreigners can only contribute up to S$35,700. This means that you cannot get the indefinite amount of tax savings that you always dream of.
- While you may withdraw SRS funds anytime, do take note that there is a 5% penalty charge if any withdrawal is made before the statutory retirement age (currently age 62). In addition, you will have to pay taxes on 100% of the amount withdrawn. For foreigners, they will have to wait 10 years for a penalty-free lump sum withdrawal. Hence, it is important to note that putting money into your SRS account is a long-term commitment.
- The SRS account only pays 0.05% per annum, which pales in comparison to CPF which generates 2.5% annually. The interest that one earns on the SRS account may not be good enough to fight inflation. But fret not – read on, and we will show you how that money in your SRS account can achieve much better returns!
Don’t let your SRS money stay idle!
Putting money into your SRS account does not mean you have to leave it out of sight, out of mind. We highly encourage you to invest your SRS monies to beat the inflation monster! In fact, there is actually a wide range of SRS-approved investment products that can help make your money work even harder. It is not too late to start on your SRS journey, but you really have to start now, srs-ly!
Investors should take a long-term approach to their investments, especially as the aim of investing with SRS funds is to plan for a more comfortable retirement. This includes diversifying your portfolio and avoiding unnecessary risks. Below are some Singapore stock counters that you may consider using your SRS monies to start investing!
SATS is a leading provider of gateway services and food solutions in the region, with over 70 years of experience and a growing regional presence. The company caters to the needs of the aviation sector and other businesses ranging from food, healthcare, hospitality, freight and logistic industries. SATS’ Q2 FY2022 revenue grew 27.2% year-on-year to S$293.9 million on the back of stronger cargo and non-travel food performances.
SingTel is one of Asia’s leading communications technology groups, providing services from next-generation communication to technology services and infotainment to both customers and businesses. It has a presence in Asia, Australia and Africa, reaching over 740 million mobile customers in 21 countries. Meanwhile, its business presence in infrastructure and technology services spans 21 countries, with over 428 direct points in 362 cities. The company’s H1 2022 results showed good momentum, with notable strength in Australia Consumer and Airtel’s turnaround.
Ascendas Reit is Singapore’s first and largest listed business space and industrial Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT), with a portfolio diversified across four major segments including business spaces, logistics and distribution centres, industrial properties and data centres. It has assets in Australia and UK, and completed the acquisition of 28 business park properties in the US in December 2019. It is managed by Ascendas Fund Management Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of CapitaLand Limited, one of Asia’s largest diversified real estate groups.
This article is written and presented by OCBC.
Disclaimer
This information is intended for general circulation and/or for discussion purposes only. All views or information expressed or provided in this article belong to and are that of the writers from OCBC and are for information purposes only. They do not take into account the specific objectives, financial situation or particular needs of any particular person. You should not make any decisions without independently verifying or assessing the contents. OCBC Securities Private Limited (“OCBC Securities”) does not endorse any view or information provided in this article and makes no representation or warranty whatsoever in respect of any view or information expressed or provided in this article. OCBC Securities shall not be responsible for any loss or damage whatsoever arising, directly or indirectly, howsoever as a result of any person acting on any view or information expressed or provided in this article.




